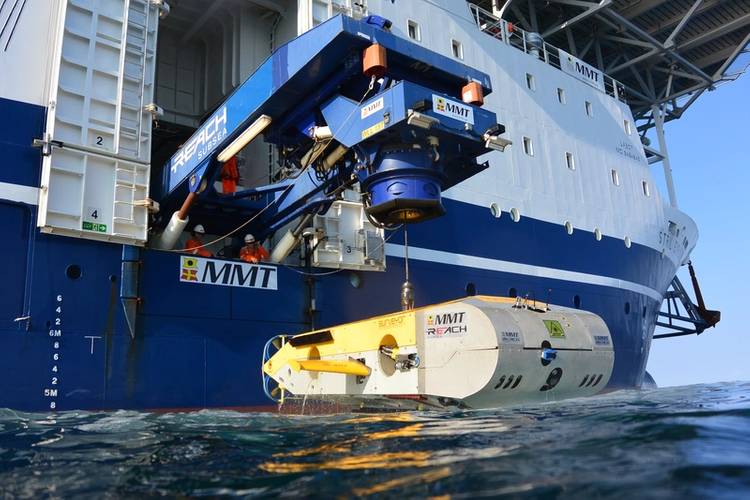
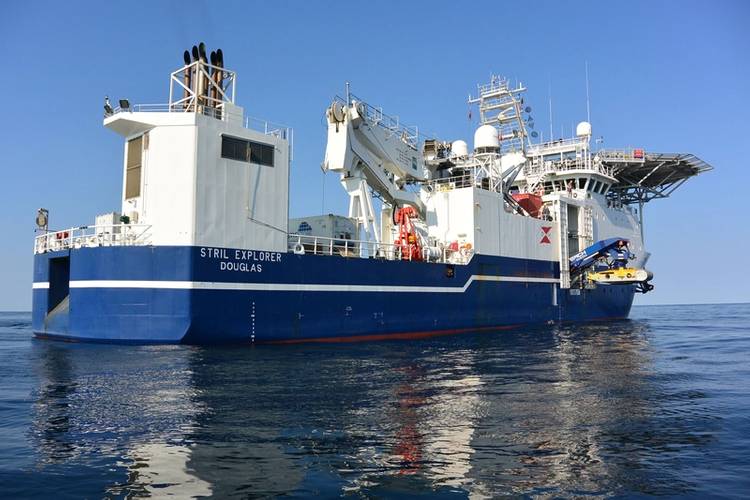
During MMT’s participation in the MAP project, the Surveyor Interceptor ROV (SROV) was used for geophysical surveys to detect former land surfaces buried below the current seabed and set new records for both depth of 1,800 meters and sustained speed over 6 knots and covered a distance of 1,000 km.
MMT founder and CTO Ola Oskarsson, who has developed SROV together with partners, explained the importance of showing the wide range of SROV’s capabilities. It was developed for the oil and gas industry but is capable to inspect and explore various seabed mapping projects, Oskarsson said, adding that the new depth and speed records is a great success for the company.
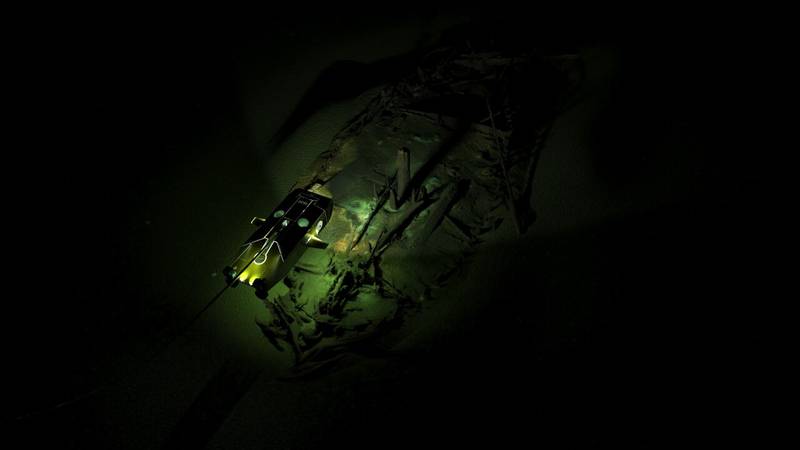
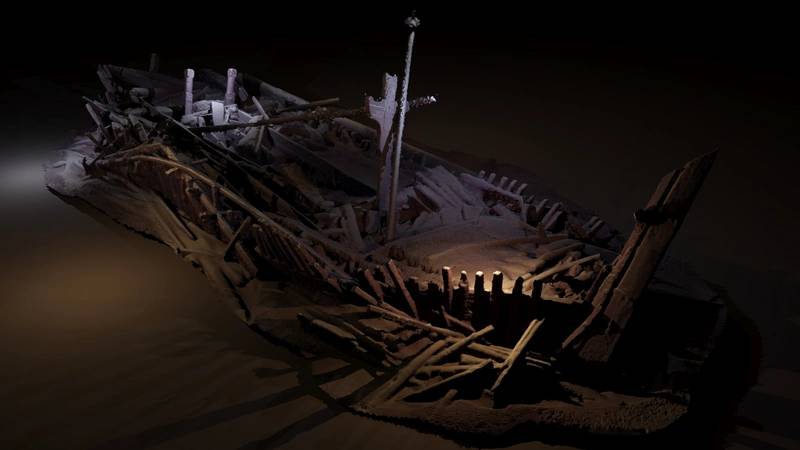
Down to 1,670 meters below the surface in the Black sea, over 40 shipwrecks were found and some had never been seen before. Thanks’ to the anoxic conditions of the Black Sea the preservation was astonishing. This expedition provided new data on the maritime interconnectivity of Black Sea coastal communities and manifest ways of life and seafaring that stretch back into prehistory.
MMT said it has a long association with the Academy at an international level and support maritime research projects through exchange of knowledge and resources. The MAP project showed just how effective partnerships between academia and industry can be.
• 






















 February 2024
February 2024



