
Aquajet to Launch New Hydrodemolition Robot Series
applications where both reach and maneuverability are essential.The 450 series is fully compatible with Aquajet’s new Aqua Rail system, as well as a range of attachments and high-pressure pumps, including the Ecosilence. The robots also integrate seamlessly with Aquajet’s EcoClear wastewater treatment system, a fully automated solution that allows on-site water treatment and recirculation, ensuring environmentally responsible operations

Opinion: Stronger Regulations Needed to Protect Our Oceans
among those ever sailed on a commercial vessel and even some regulatory bodies, yet its impact on our marine ecosystems is devastating.The MARPOL Convention, which governs ship pollution, is simply not enough. The regulations allow ships to meet minimal standards, enabling them to operate with wastewater treatment systems that fail to properly handle harmful substances. These ships continue to release pollutants such as black, grey and oily water into the oceans for decades, contributing to long-term environmental degradation.Weak Regulations, Weak SolutionsOne might point out that there are fewer detentions

Academia’s Climate Change Challenge is Far from Academic
the factors involved are complex—physical parameters include depth, currents, tides and temperatures—the findings show that a mussel-based cleaning system could provide positive effects in estuarine areas, especially in places were microplastics may accumulate, like harbors or near wastewater treatment plants. “Ultimately, we need to be thinking about making plastics part of a circular economy, where end-of-life plastic is reused, recycled or safely disposed,” said Lindeque. “In the meantime, we hope that by using natural ecosystems and processes, like the mussels'

Long Island Sound Water Quality Improving
resulting from almost 50 million pounds of nitrogen pollution kept out of the Sound each year. A peer-reviewed study from the University of Connecticut published earlier this year showed that improved water quality can be attributed to successful programs in Connecticut and New York to upgrade wastewater treatment plants to remove nitrogen before treated sewage is discharged into the Sound.These two state-led programs have reduced millions of pounds of nitrogen pollution from being discharged into Long Island Sound, which has led to increased oxygen concentrations in the Sound in the summer months and

New Study Finds Polyester Fibers Throughout the Arctic Ocean
Ocean from the Atlantic than the Pacific.The size, shape, colors and polymer identity of the majority of these particles provide additional indications of their origins. These physical characteristics closely resembled what we encountered in our 2018 study of microplastics in the largest domestic wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver.The size and shape of these fibers also closely mirrored those observed in laundry effluent, and builds on a series of studies showcasing the vulnerability of textiles to shedding during home laundry. In fact, we recently estimated that the average Canadian or U.S. household
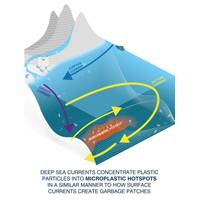
SCIENCE: Seafloor Microplastic Hotspots Controlled by Deep-sea Currents
are not uniformly distributed across the study area; instead they are distributed by powerful seafloor currents which concentrate them in certain areas.”Microplastics on the seafloor dominantly comprise fibers from textiles and clothing. These are not effectively filtered out in domestic wastewater treatment plants, and easily enter rivers and oceans. In the ocean they either settle out slowly, or can be transported rapidly by episodic turbidity currents – powerful underwater avalanches – that travel down submarine canyons to the deep seafloor (see the group’s earlier research
Cruise Lines Invests $22 Bln in Clean Fuel Tech
exceed air emissions requirements representing an increase in capacity of 17% compared to last year, the report revealed.Additionally, 75% of non-LNG new builds will have EGCS installed, an increase in capacity of 8% compared to last year.100% of new ships on order are specified to have advanced wastewater treatment systems (an increase of 26% over 2018) and currently 68% of the CLIA Cruise Lines global fleet capacity is served by advanced wastewater treatment systems (an increase of 13% over 2018).In port, cruise ships are increasingly equipped with the technology to allow delivery of shoreside electricity

Average Sized Dead Zone Expected in the Gulf of Mexico
in the water. The resulting low oxygen levels near the bottom are insufficient to support most marine life.Studies have also shown a multitude of other impacts associated with high nutrient concentrations within watersheds. Such impacts include high nitrates in groundwater, higher drinking and wastewater treatment costs and wasted fertilizer applications.“The Gulf’s recurring summer hypoxic zone continues to put important habitats and valuable fisheries at risk,” said Steve Thur, Ph.D., director of NOAA’s National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science. “Although there has been

Almarin Buoys Reach New Markets
estuary in Beirut (Lebanon), several buoys have been supplied complete with moorings and self-contained lanterns to provide safe navigation. Almarin has also supplied buoys in other parts of Lebanon, for example, Balizamar buoys were Veolia’s choice to mark the sea outfall at Ras Nabi Younis Wastewater Treatment Plant. In this case the buoys were provided complete with a monitoring system linked to an online platform that allows the customer to know the status and position of the buoy and lantern at any time as well as a series of pre-determined alarms. Algeria, in the North African Mediterrenean


 February 2025
February 2025





