The Ocean and its role in Unusual Temperature Changes
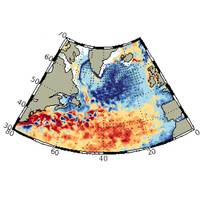
A study by scientists at the National Oceanography Center (NOC) published in Nature Communications Earth and Environment, reveals that the ocean is as important as the atmosphere in causing unusual temperature variations in the subpolar North Atlantic. Furthermore, it shows that the ocean’s contribution has strengthened over the past 60 years at the expense of the atmosphere, pointing to the need for greater understanding of the ocean’s role in setting North Atlantic and European climate variability.The study by Simon Josey and Bablu Sinha, with UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) funding

NOC-led Study Paves the Way for Future Climate Models
The National Oceanography Center (NOC) has led a study to investigate gaps in knowledge of the biological carbon pump, in the hope of prioritizing which aspects should be included in future climate model developments, and the observations necessary to achieve that. The study, which was carried out with the Imperial College, University of Washington, University of Bern and Boston College is aiming to pave the way for more accurate modelling of future ocean carbon storage.Climate models aim to inform us about how the world will respond to climate change caused by increasing carbon dioxide in the atmospher

Ensnared, Endangered Green Sea Turtle Rescued
Best known for housing the third largest barrier reef in the world, Andros Island in the Bahamas boasts a diverse marine population amid pristine waters. It’s perhaps less well known to serve as home to NUWC Division Newport’s Atlantic Undersea Test and Evaluation Center (AUTEC).On July 13, these two worlds collided when a large endangered green sea turtle was found ensnared by fishing lines and nets in AUTEC’s harbor.Mike Beres, a member of the AUTEC Fire and Emergency Services Water Rescue Team, spotted the entangled turtle and noticed that it was struggling to surface for air

GOM Geotechnical Coring Program Completed for NOAA OER Expedition
TDI-Brooks was contracted by Coastal Environments Inc. and Gray & Pipe, Inc. who received funding from NOAA’s Office of Ocean Exploration and Research for this expedition. TDI-Brooks performed geotechnical piston coring at Sabine Pass 6 and High Island Blocks 117, 118, 130, 160, 177, 178 and A7. These efforts are part of the expedition “Paleolandscapes and the ca. 8,000 BP Shoreline of the Gulf of Mexico Outer Continental Shelf 2020”, to add more information about the environment in which early Gulf Coast inhabitants would have lived.The original geophysical data collected in the


 February 2025
February 2025





