
Rapid Loss of Antarctic Ice Might Signal Climate Tipping Point
Rapid loss of Antarctic sea ice could be a tipping point for the global climate, causing sea level rises, changes to ocean currents and loss of marine life that are impossible to reverse, a scientific study published on Thursday said.The paper in the journal Nature aimed to describe in previously unseen detail the interlocking effects of global warming on the Antarctic, the frozen continent at the planet's South Pole."Evidence is emerging for rapid, interacting and sometimes self-perpetuating changes in the Antarctic environment," it said.The study gathered data from

Hanwha Ocean Selected as Preferred Bidder for Icebreaking Research Vessel
to be a 'completely new icebreaking research platform,’" said an official from Hanwha Ocean. "This ship will bring to focus the core competencies of Hanwha Ocean as a top-tier global shipyard."Looking forward, Hanwha Ocean will continue to build icebreaking research vessels. As Arctic Sea ice melts faster than expected, the region is becoming a hot bed for resources, logistics and technology, not just new shipping routes. As such, Hanwha Ocean plans to quickly develop icebreakers as one of its future growth engines.Meanwhile, Hanwha Ocean's Product Strategy & Technology

Arctic Sea Ice Hits Record Low Maximum Extent for the Year
Arctic sea ice has likely reached its maximum extent for the year, at 14.33 million square kilometers (5.53 million square miles) on March 22, according to scientists at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder.The 2025 maximum sea ice extent is the lowest in the 47-year satellite record, falling short of the previous record low of 14.41 million square kilometers (5.56 million square miles) set on March 7, 2017.“This new record low is yet another indicator of how Arctic sea ice has fundamentally changed from earlier decades,” said NSIDC senior

A Graveyard for Glaciers
mark the first-ever World Day for Glaciers.To coincide with this, the World Meteorological Organization released its State of the Global Climate report. It comes before World Glaciers Day on March 21, World Water Day on March 22 and World Meteorological Day on March 23. It states:• The 18 lowest Arctic sea-ice extents on record were all in the past 18 years.• The three lowest Antarctic ice extents were in the past three years.• The largest three-year loss of glacier mass on record occurred in the past three years.• In 2024, global mean sea level reached a record high in the satellite

WMO Documents Spiraling Climate Impacts
that:• Atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide are at the highest levels in the last 800,000 years.• Globally each of the past 10 years were individually the 10 warmest years on record.• Each of the past eight years has set a new record for ocean heat content.• The 18 lowest Arctic sea-ice extents on record were all in the past 18 years.• The three lowest Antarctic ice extents were in the past three years.• The largest three-year loss of glacier mass on record occurred in the past three years.• The rate of sea level rise has doubled since satellite measurements

Ice Navigation: Every Voyage is Different
coarse spatial resolution. Deploying human-crewed ships is difficult due to extreme weather conditions. AUVs are hindered by energy constraints that restrict their research potential.Still, satellites have continuously monitored the Earth’s polar regions since November 1978, and over that period, Arctic sea ice has declined.Since 2014, Antarctic sea ice has exhibited both record-high and record-low extents. From 2013 through 2015, Antarctic sea ice extent was mostly above average. In September 2023, the Antarctic winter maximum set a record low by a wide margin. The low Antarctic sea ice extent through
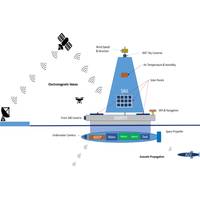
Autonomous Multi-Vehicle System Designed for Long-Term Arctic Studies
.“Our researchers have developed an innovative observation system tailored to the Arctic environment, offering critical data on sea ice melt that satellites and manned vessels are unable to capture. Long-term monitoring is essential, as it provides deeper insights into the lasting impacts of Arctic sea ice loss, which can guide informed policy and management decisions,” said Stella Batalama, Ph.D., dean of the FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science. “Additionally, there remains much to uncover about Arctic phytoplankton and algae, which play a crucial role in the food web

Arctic Sea Ice Could Reach Turning Point by 2027
. The team used computer models to predict when the first ice-free day could occur in the northernmost ocean.When the Arctic Ocean has less than 1 million square kilometers of ice, scientists say the Arctic is ice free.In September, the National Snow and Ice Data Center reported that this year’s Arctic sea ice minimum, the day with the least amount of frozen seawater in the Arctic, was one of the lowest on record since 1978.At 1.65 million square miles, or 4.28 million square kilometers, this year’s minimum was above the all-time low observed in September 2012, but it still represents a stark
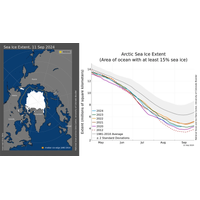
Arctic Sea Ice Reaches Seventh Lowest Extent on Record
Arctic sea ice has likely reached its minimum extent for the year, at 4.28 million square kilometers (1.65 million square miles) on September 11, 2024, according to scientists at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder.The 2024 minimum is ranked seventh lowest in the 46-year satellite record. The last 18 years are the lowest 18 Arctic sea ice extents in the satellite record.The overall, downward trend in the minimum extent from 1979 to 2024 is 12.4 percent per decade relative to the 1981 to 2010 average. From the linear trend, the loss of sea ice is about 77
 February 2026
February 2026





