High-Risk Litter Zones Threaten North Atlantic Wildlife
A new study, led by Plymouth Marine Laboratory, has revealed five high-risk zones where floating plastic litter poses the greatest risk to North Atlantic marine life.
An estimated 19 to 23 metric tons of plastic waste entered the world's aquatic ecosystems in 2016 and this figure is predicted to triple by 2030.
Land-based sources of plastic are thought to account for about 80% of plastic pollution in the marine environment, with single use items such as plastic bags, bottles, wrappers, food containers and cutlery among the most common items found. These items are often transported far from their original source via a complex system of ocean currents, making this transboundary pollutant even more challenging to monitor and manage.
Over 4,000 marine and coastal species are known to be affected in some way by marine plastic debris, with some species more sensitive to plastic pollution than others and therefore, at greater risk.
This study assessed the risks of land-derived plastic litter to major groups of marine megafauna (seabirds, cetaceans, pinnipeds, elasmobranchs, turtles, sirenians, tuna and billfish) and a selection of productive and biodiverse habitats (coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass, saltmarsh and kelp beds).
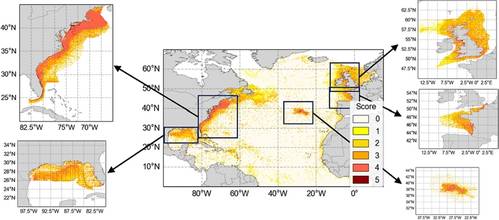
The team modelled the transport of plastic from 16 countries surrounding the North Atlantic, releasing billions of virtual plastic particles from rivers between 2000 to 2015. The movement of these particles was driven by surface currents and wind, and after a 15 year run, the model showed where plastic was accumulating.
To assess risk, modelled plastic concentrations were combined with the distribution and vulnerability of various megafauna groups and shallow water habitats. Vulnerability scores were devised by assessing the extent of documented ingestion, entanglement or smothering of land-based plastic.
The modelling analysis identified high-risk zones (HRZs) as UK waters, the Azores, the French and US Atlantic coasts and the US Gulf of Mexico.
Whilst much of the land-derived plastic litter influencing risk in UK territorial waters originated from UK rivers, in other HRZs, such as the Azores archipelago and the US Gulf of Mexico, plastic originated from other regions, with most of the plastic in the Azores estimated to have come from the Caribbean and US.
Land-derived plastic litter from the Caribbean islands, some of the largest generators of marine plastic pollution in the dataset of river plastic emissions used in the study, was noted as a significant input to HRZs across both sides of the Atlantic.
The marine megafauna most at risk were shown to be seabirds, cetaceans (whales, dolphins and porpoises), turtles and elasmobranchs (sharks, rays, skates). Sheet-like plastics such as plastic bags and food wrappers were the most commonly ingested type of land-derived plastic litter for most marine megafauna, except seabirds which were generally more at risk of ingesting hard plastic fragments.
The habitats most at risk were mangroves and coral reefs, both of which are ecologically-important as refuge and nursey grounds whilst also providing coastal protection. Entanglement and smothering by plastic appear to be a significant threat for these habitats, with entanglement causing both breakage and disease in corals, and breakage in mangrove branches and roots. Smothering of corals and mangrove branches, roots or saplings by land-sourced plastic led to frequent mortality in corals, and a reduction in tree density in mangroves.
Dr Sam Garrard, lead author of the study and Marine Ecosystem Services Researcher at Plymouth Marine Laboratory, said: “These findings highlight the potential of Spatial Risk Assessment analyses to determine the location of high-risk zones and understand where plastic debris monitoring and management should be prioritised, enabling more efficient deployment of interventions and mitigation measures.”
UN member nations have consented to forge an international legally-binding agreement to tackle plastic pollution, called the Global Plastics Treaty, with negotiations expected to be completed by the end of this year. “This study highlights the importance of the treaty in ensuring international cooperation to reduce plastic consumption and waste, including the provision of financial support to help lower-income nations, such as the Caribbean islands, implement measures.”










 February 2026
February 2026



