NSF Grant to Enhance Satellite-derived Bathymetry Technology
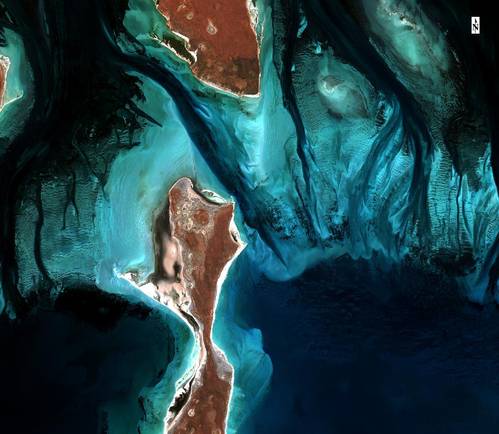

TCarta will deploy machine learning and computer vision techniques to enhance satellite derived bathymetry in the littoral zone. (Image source: Copernicus Sentinel data 2018)
Marine geospatial products provider TCarta Marine has been awarded a research and development grant by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to enhance and automate multiple techniques for deriving seafloor depth measurements from optical satellite imagery. The ‘Project Trident’ research seeks to transform existing satellite derived bathymetry (SDB) techniques by leveraging machine learning and computer vision technology to enable accurate depth retrieval in variable water conditions.
If successful, TCarta said, these enhanced bathymetric techniques will have positive impacts on operations related to oil and gas exploration and production, coastal infrastructure engineering, environmental monitoring, and geointelligence (GEOINT) activities.
“Our goal with Project Trident is to expand the geographic scope of SDB in shallow coastal areas,” said Kyle Goodrich, TCarta President. “SDB technology currently derives water depths only in calm, clear waters, which limits its applicability.”
TCarta won the grant for Project Trident in partnership with jOmegak of San Carlos, Calif., and DigitalGlobe of Westminster, Colo., in Phase 1 of the NSF Small Business Innovation Research program. The one-year research project will be carried out at the TCarta facility in Denver.
In 2014, TCarta successfully commercialized a proprietary technique for digitally extracting water depth measurements down to 20 meters from high-resolution DigitalGlobe WorldView satellite imagery. The SDB products became popular with organizations operating in shallow coastal waters because the technology is more cost-effective and timely than traditional airborne and ship-borne bathymetric methods – with no adverse effects on the environment.
“In the current SDB process, we use manual stereo photogrammetry methods to measure seafloor ground control points in digital satellite imagery, but this is extremely time consuming,” said Goodrich. “We are developing an automated photogrammetric process to extract a greater number of ground truth points from high-resolution WorldView imagery.”
Project Trident aims to integrate wave kinematics, a technique patented by jOmegak to calculate water depths in shallow waters by analyzing the patterns and speed of waves detected in satellite imagery. Wave kinematics has been applied successfully using Sentinel-2 and WorldView satellite imagery.
“Thanks to the NSF grant, we are taking a giant leap forward on TCarta satellite-derived bathymetry methodologies and aim to exponentially accelerate them with the latest in machine learning and computer vision technologies,” said Goodrich.
The company is now soliciting beta testers for participation in Project Trident research.












 August 2025
August 2025



