
'Blue Economy' Target of Government Funding
impact of removing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and storing it in the deep ocean.Hazard mitigation and coastal resilience to improve wind and water level predictions that help prepare for and reduce beach erosion, coastal flooding, and — most important — prevent loss of human life.Ecosystem Services to accurately assess and forecast ecosystem changes, like shifts in species location, marine heat waves or changes in sea level and to support decision makers, including natural resource managers, offshore operators, permitting agencies and others who require the best available science, data

Restoring Marine Habitats and Port Decarbonization
seagrass meadows: Efficiency and ecological implications. Restoration Ecology, 29, e13313.22.Orth, R., Lefcheck, J., McGlathery, K., Aoki, L., Luckenbach, M., Moore, K., Oreska, M., Snyder, R., Wilcox, D., & Lusk, B. (2020). Restoration of seagrass habitat leads to rapid recovery of coastal ecosystem services. Science Advances, 6.23.https://sciencebasedtargetsnetwork.org/how-it-works/the-first-science-based-targets-for-nature/24.https://naturalengland.blog.gov.uk/2023/12/11/government-takes-a-step-forward-for-marine-nature-recovery/25.Greaves, D., Attrill, M., Chadwick, A., Conley, D., Eccleston

The Potential of Restoring Marine Habitats
seagrass meadows: Efficiency and ecological implications. Restoration Ecology, 29, e13313.22.Orth, R., Lefcheck, J., McGlathery, K., Aoki, L., Luckenbach, M., Moore, K., Oreska, M., Snyder, R., Wilcox, D., & Lusk, B. (2020). Restoration of seagrass habitat leads to rapid recovery of coastal ecosystem services. Science Advances, 6.23.https://sciencebasedtargetsnetwork.org/how-it-works/the-first-science-based-targets-for-nature/24.https://naturalengland.blog.gov.uk/2023/12/11/government-takes-a-step-forward-for-marine-nature-recovery/25.Greaves, D., Attrill, M., Chadwick, A., Conley, D., Eccleston

RWE Deploys Artificial Reefs at Offshore Wind Farm in the Baltic Sea
vary from 15x15 cm to 75x75 cm in size, have been installed at the 48 MW Kårehamn offshore wind farm, which features 16 turbines located 7 km off the Swedish coast.The objective of the study is to assess how artificial structures at offshore wind farms can promote biodiversity and support ecosystem services, such as habitat provision, nutrient cycling and water quality, hence contributing to the restoration and preservation of the Baltic Sea.The study started in 2023 with the collection of information for the baseline scenario. This included a survey of the underwater area including sampling from
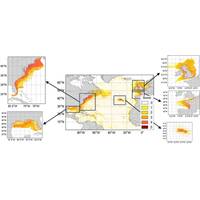
High-Risk Litter Zones Threaten North Atlantic Wildlife
breakage and disease in corals, and breakage in mangrove branches and roots. Smothering of corals and mangrove branches, roots or saplings by land-sourced plastic led to frequent mortality in corals, and a reduction in tree density in mangroves.Dr Sam Garrard, lead author of the study and Marine Ecosystem Services Researcher at Plymouth Marine Laboratory, said: “These findings highlight the potential of Spatial Risk Assessment analyses to determine the location of high-risk zones and understand where plastic debris monitoring and management should be prioritised, enabling more efficient deployment

Speaker Line-Up for Catch the Next Wave’s Return at Oi24
aims to spark new thinking and ideas across disciplinary boundaries and between sectors, taking a futuristic look at how key areas of rapidly evolving technology might help to achieve net zero and beyond, at the same time as supporting the restoration of the Earth’s essential biodiversity and ecosystem services.CTNW speaker and conference committee member Jyotika Virmani, said: “I have been part of Catch the Next Wave for many years and what I find fascinating and wonderful about Catch the Next Wave is that it is the only conference which pairs together what is happening in marine technology

Discover the Future of Ocean Tech: Oi24 Event Registration Now Live
crisis. It will take a futuristic look at how key areas of rapidly evolving technology might contribute to innovative solutions at the ocean-climate nexus, helping to achieve net zero and beyond, at the same time as supporting the restoration of the Earth’s essential biodiversity and ecosystem services. Topics include: The Energy Transition; Climate Repair; Protecting the Earth’s Living Systems; Innovating the Ocean Economy of the Future

US Awards $6.7 Million for Sea Level Rise and Coastal Resilience Research
$500,000 to evaluate how different shoreline adaptation actions perform with sea level rise and storms in California.University of Rhode Island and Penn State University received over $360,000 to assess how nature-based solutions reduce coastal vulnerability to sea level rise while preserving ecosystem services in Rhode Island.(IRA-funded) U.S. Geological Survey and University of California Santa Cruz received over $324,000 to evaluate flood risk in linked coral and mangrove ecosystems in the U.S. Virgin Islands.NCCOS is also funding projects through annual appropriations to improve coastal community

NOAA to Award $28 Million to Tackle Marine Debris
debris requires coordination and collaboration with partners across the country, and we are excited to advance projects that support partnerships and solutions.”“These funding opportunities will support transformational projects that benefit our public trust natural resources and the ecosystem services that they provide,” said Nancy Wallace, director of the NOAA Marine Debris Program. “This funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law will allow us to address the marine debris that is most challenging to remove and damaging to our waterways, ocean and Great Lakes.”The


 February 2025
February 2025





