Abundant Life Found on Seamounts Off Chile’s Coast
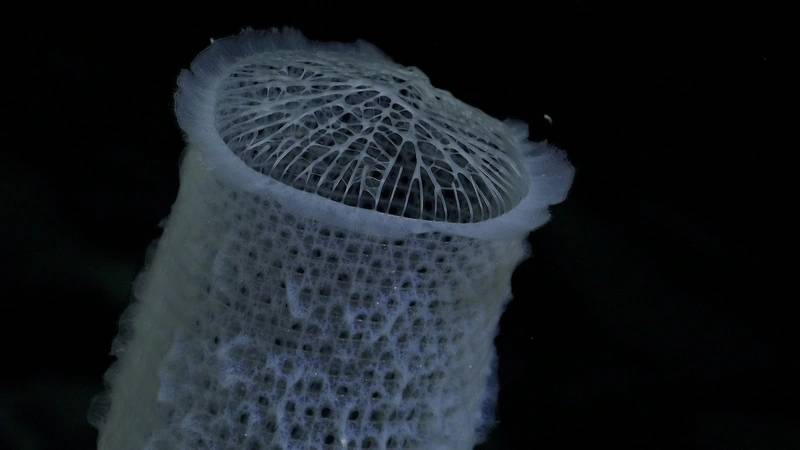
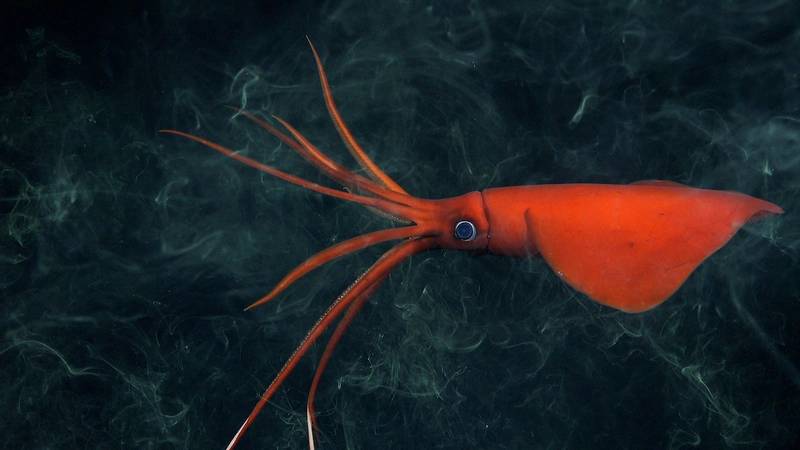
An international group of scientists, led by Dr. Javier Sellanes of the Universidad Católica del Norte, may have discovered more than 100 new species living on seamounts off the coast of Chile. The recent Schmidt Ocean Institute expedition resulted in finding deep-sea corals, glass sponges, sea urchins, amphipods, squat lobsters, and other species likely new to science.
The team explored seamounts along the Nazca and Salas y Gómez Ridge, both inside and outside Chile’s jurisdiction, to collect data that could support the designation of an international high-seas marine protected area. The Salas y Gómez Ridge is a 2,900-kilometer-long underwater mountain chain comprising more than 200 seamounts that stretch from offshore Chile to Rapa Nui, also known as Easter Island. The majority of the ridge exists outside national jurisdiction. Additionally, the scientists explored two of Chile’s marine protected areas, the Juan Fernandez and Nazca-Desventuradas marine parks.
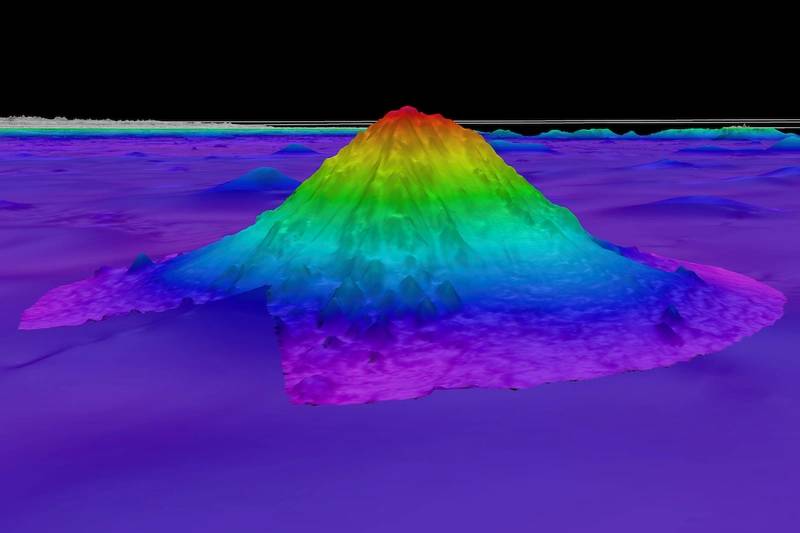
During the expedition, scientists used an underwater robot, capable of descending to depths of 4,500 meters, to collect data from 10 seamounts that will be used to advance Chile’s marine protection efforts. The scientists found that each seamount hosted distinct ecosystems, many of which are vulnerable, including thriving deep-sea coral reefs and sponge gardens. The scientists are analyzing the physiology and genetics of the specimens they suspect are new to science to confirm if they are new species.
Experts on board the ship mapped 52,777 square kilometers of seafloor, resulting in the discovery of four seamounts within Chilean waters. The fourth seamount, the tallest mountain at 3,530 meters, was explored for the first time, mapped, and unofficially named Solito by the science team.
“We far exceeded our hopes on this expedition. You always expect to find new species in these remote and poorly explored areas, but the amount we found, especially for some groups like sponges, is mind-blowing,” said Sellanes. “These thriving and healthy ecosystems indicate that the Nazca-Desventuradas and Juan Fernández Marine Parks effectively protect delicate marine habitats.”

A second expedition along the Salas y Gomez Ridge will begin aboard research vessel Falkor (too) on February 24. Underwater dives will be livestreamed on Schmidt Ocean Institute's YouTube channel as scientists explore areas deeper than 600 meters for the first time. Schmidt Ocean Institute will be operating in the Southeast Pacific, exploring the waters off Peru and Chile throughout 2024.
“Full species identification can take many years, and Dr. Sellanas and his team have an incredible number of samples from this amazingly beautiful and little-known biodiversity hotspot,” said Schmidt Ocean Institute Executive Director Dr. Jyotika Virmani. “Schmidt Ocean Institute is a partner with the Nippon Foundation - Nekton Ocean Census Program, which has set a target of finding 100,000 new marine species in the next 10 years and, once identified, these new species will be a part of that.”















 February 2026
February 2026



