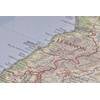
Florida Current is the Weakest Its Been in a Century

A new study uses a method of tracking the strength of near-shore ocean currents from a distance via measurements of coastal sea level. (Photo by Carol Anne Clayson, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
The Florida Current, which forms the start of the Gulf Stream, has slowed over the past century and is the slowest it has been at any point in the past 110 years, a new study reveals.
Researchers have developed a method of tracking the strength of near-shore ocean currents using measurements made at the coast, offering the potential to reduce one of the biggest uncertainties related to observations of climate change over the past century.
“In the ocean, almost everything is connected,” said Christopher Piecuch, an assistant scientist in the Physical Oceanography Department at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and author of the study published Friday in Nature Communications. “We can use those connections to look at things in the past or far from shore, giving us a more complete view of the ocean and how it changes across space and time.”
Piecuch, who specializes in coastal and regional sea level change, used a connection between coastal sea level and the strength of near-shore currents to trace the evolution of the Florida Current, a key component of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream flows north along the Southeast Atlantic Coast of the United States and eventually east into the North Atlantic Ocean, carrying heat, salt, momentum and other properties that influence Earth’s climate. Because nearly continuous records of sea level stretch back more than a century along Florida’s Atlantic Coast and in some parts of the Caribbean, he was able to use mathematical models and simple physics to extend the reach of direct measurements of the Gulf Stream to conclude that it has weakened steadily and is weaker now than at any other point in the past 110 years.
One of the biggest uncertainties in climate models is the behavior of ocean currents either leading to or responding to changes in Earth’s climate. Of these, one of the most important is the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which is a large system or “conveyor belt” of ocean currents in the Atlantic that includes the Gulf Stream and that helps regulate global climate. Piecuch’s analysis agrees with relationships seen in models between the deeper branches of the AMOC and the Gulf Stream, and it corroborates studies suggesting that the deeper branches of AMOC have slowed in recent years. His method also offers the potential to monitor ocean currents like the Gulf Stream from the coast, complementing existing but difficult-to-maintain moored instruments and expensive research cruises.
“If we can monitor something over the horizon by making measurements from shore, then that’s a win for science and potentially for society,” Piecuch said.




![Microplastic beads seen in the central tube of a copepod [their intestinal tract], as evidenced here, fluorescently labelled beads help with visualization and identification. © PML](https://images.marinetechnologynews.com/images/maritime/w100h100padcanvas/microplastic-beads-seen-166795.jpeg)










 December 2025
December 2025



